‘path’ elements, ‘text’ elements and shapes can be filled (which means painting the interior of the object) and stroked (which means painting along the outline of the object). Iin this tutorial:
SVG Fill
The fill of an SVG shape defines the color of the shape inside its outline (the surface of the SVG shape). You can set the fill for any SVG shape.
Fill atributes are:
- fill: the method of filling the area with a solid colour, gradient, pattern. The value none indicates that the area is not to be filled.
- fill-opacity: is used to set the opacity of the fill color of a shape. The fill-opacity takes a decimal number between 0 and 1.
- fill-rule: for complex paths, the definition of the area to be filled. Takes two values:
- evenodd: the number of intersections that a line between a point and infinity makes with the path are counted. If the number is odd, the point is inside the area and should be filled.
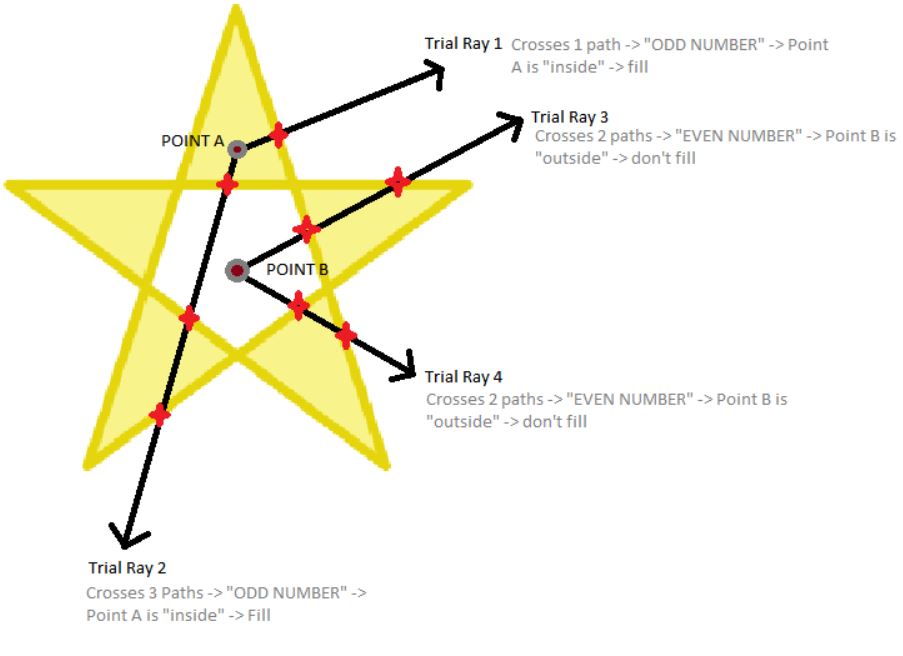
- nonzero: the number of times the path winds around a point is counted.
One is added each time a path segment crosses the line from left to right (clockwise) and one is subtracted each time a path segment crosses from right to left (counterclockwise).
If the number is nonzero, the point is inside.
- evenodd: the number of intersections that a line between a point and infinity makes with the path are counted. If the number is odd, the point is inside the area and should be filled.
Example:
<svg>
<path d="M50,20 l40,40 l-40,40 l-40,-40 l40,-40
M50,40 l20,20 l-20,20 l-20,-20 l20,-20" style="stroke: #000000;
fill: #6666ff;
fill-rule: nonzero;" />
<path d="M150,20 l40,40 l-40,40 l-40,-40 l40,-40
M150,40 l-20,20 l20,20 l20,-20 l-20,-20" style="stroke: #000000;
fill: #6666ff;
fill-rule: nonzero;" />
</svg>
The nonzero rule considers the inner diamond inside or outside the shape depending on the direction the inner diamond is drawn.
In the following examples arrows indicate the direction of the path.
nonzero fill examples:
evenodd fill examples:
SVG Stroke
A subset of the complete set of stroke properties is:
- stroke: the method of rendering the outline with a solid colour or gradient. The possible values are the same as for the fill property. A value of 'none' indicates that no outline is to be drawn.
- stroke-width: defines the width of the outline.
- stroke-dasharray: defines the style of the line (dotted, solid, dashed etc).
- stroke-dashoffset: for a dashed line, indicates where the dash pattern should start.
- stroke-linecap: defines the way the end of a line is rendered (butt, round, or square).
- stroke-linejoin: defines how the join between two lines is rendered (miter, round, or bevel).
- stroke-miterlimit: places some constraints on mitered line joins.
- stroke-opacity: defines the opacity of the outline. Number from 0 to 1. .

Text Stroke & Fill
Like other SVG shapes, text can have both a stroke and fill set on it. If you specify only a stroke, the text will appear as an outline of the text. If you specify only a fill, the text will look as text is rendered normally.
Example:
Example: multi-stroke
<svg width="350" height="75" viewBox="0 0 350 75">
<g style="font-size:45; font-weight: bold; font-family: Impact">
<text x="175" y="55" style="fill: white; stroke: #0f9; stroke-width: 14">Stroked Text</text>
<text x="175" y="55" style="fill: white; stroke: #99f; stroke-width: 8">Stroked Text</text>
<text x="175" y="55" style="fill: white; stroke: black; stroke-width: 2">Stroked Text</text>
</g>
</svg>