HTML
Learn & Practice
Learn & Practice

In this lecture in the HTML5 course, you will learn and practice HTML coding.
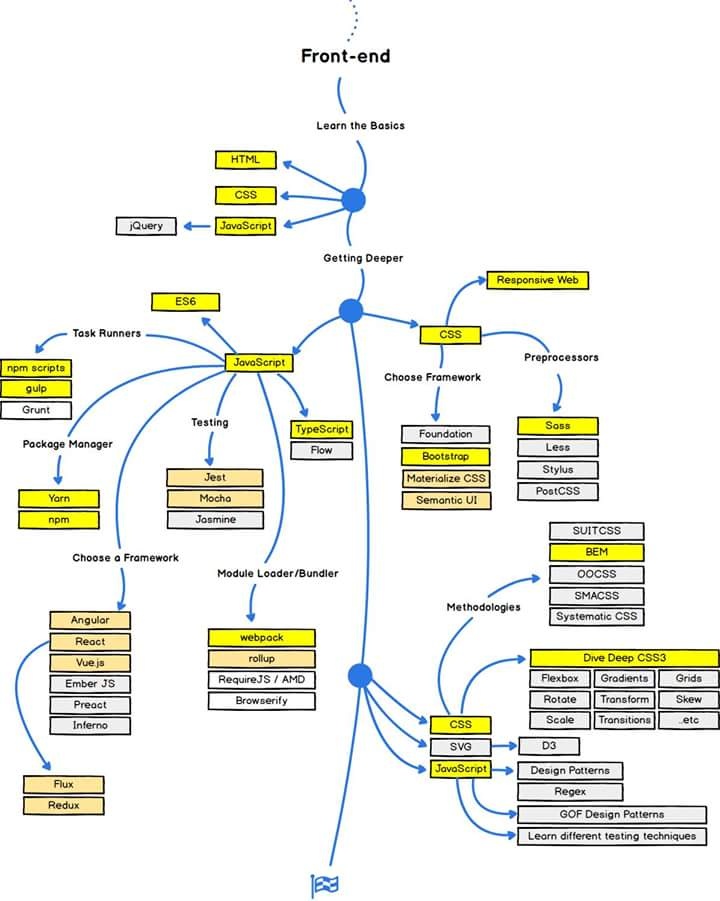
HTML, CSS and JavaScript are 3 main languages of Web Front-end Development. HTML is a language mainly used on the Internet for the content and structure of a website. A website typically consists of multiple pages, and each page is written in HTML. The visual formatting of the content written in HTML will be done with CSS. This means that in CSS we will define how our pages look. JavaScript provides a page with behavior.
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language. Hypertext means that you can embed links inside the texts. When you click the links you are taken to a different location either inside the same HTML page, or in another HTML page.
The latest version of HTML is HTML5. It was published in October 2014. HTML5 consists
of many new features, some elements and attributes have been removed, and others have been changed,
redefined or standardized.
Some examples: to handle multimedia and
graphical content, the new <video>, <audio> and <canvas> elements
were added. Support for scalable vector graphics <svg> content and MathML for
mathematical formulas was added. To enrich the semantic content of documents, HTML5
defines new page structure elements. See Why HTML5.
The term HTML5 is also used to refer grouping of "HTML5 and all its related standards, such as CSS3 and JavaScript".
Note that trends in web development sometimes change faster than they can be implemented (see What is the Future of Front End Development in 2020, Web Development Trends and the Latest Web Technology Stacks in 2019 articles).
For inspiration, see the following impressive examples with HTML5:
Students work examples:
HTML5 Basic Site
HTML5 Graphics and Animation
In this lecture we will learn the core of the HTML coding. CSS and JavaScript will be covered in other lectures.
Every web page is actually an HTML file. HTML files are simple plain-text files, so to start writing in HTML, you need a simple text editor (for example Notepad++, see more editors in the 'Sites' tab on the top menu). HTML file extension has to be .html. The first site page has to be named index.html. It will be opened when you enter the site.
When we wtite our HTML file, we can activate it in a few ways, for example, by typing its name (including the path of the file) in a browser, or opening it by double-clicking its name.
Try: Write your name in the file (let's call the file first-try.html). Then activate the file by double-clicking its name in the file folder. See how the browser displays it.
You can find code conventions in Google HTML/CSS Style Guide.
Some general rules:

Go to the next lesson in this lecture by pressing the right arrow on the bottom-left side of this page, and start exploring HTML5 syntax, tags and attributes.
Most of the pages are interactive. You can choose some predefined options from the lists. Then, you are free to change the codes or write your own to explore various HTML5 options and to see live preview of your changes.
Look at 'Tutorials' tab on the top menu for more detailed explanations about the HTML5 syntax. For the complete references, see the links in the 'Sites' tab on the top menu.
At the end of this lecture you will be able to build a site like the following.
See how to work with the demos in Site Work.
While learning and after you complete HTML lessons check yourself in:
Remember: No one can memorize everything, especially when you learn web development. Understand how you can use HTML, and how to use online resources to find html tags and attributes that you need and how to find solutions to problems.
Enjoy learning HTML!