Data binding is a way to bind some data (or an expression) to something else, such that when we change the data/expression, that something else automatically changes or is affected.
Angular supports data binding, which coordinates parts of a component template (HTML) with the code (Class). The code can provide values from the class to the template for the display, and the template can raise events to pass user actions or values to the class. The binding is done by adding special binding markup to the template HTML, which tells Angular how to connect both sides.
Angular provides several types of binding:
- inter-component - binding between the component template and the code.
- parent-child - binding inside nested components.
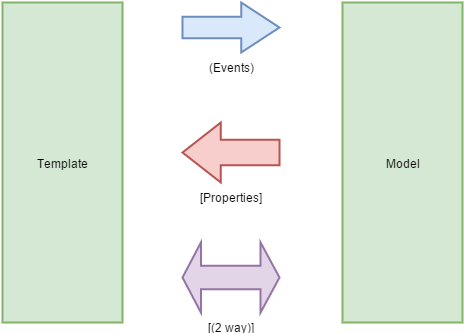
Inter-Component
inter-component is a communication between a component template (HTML) and the same component model (class). The binding includes properties and events and can go in both directions (template ⇔ model):
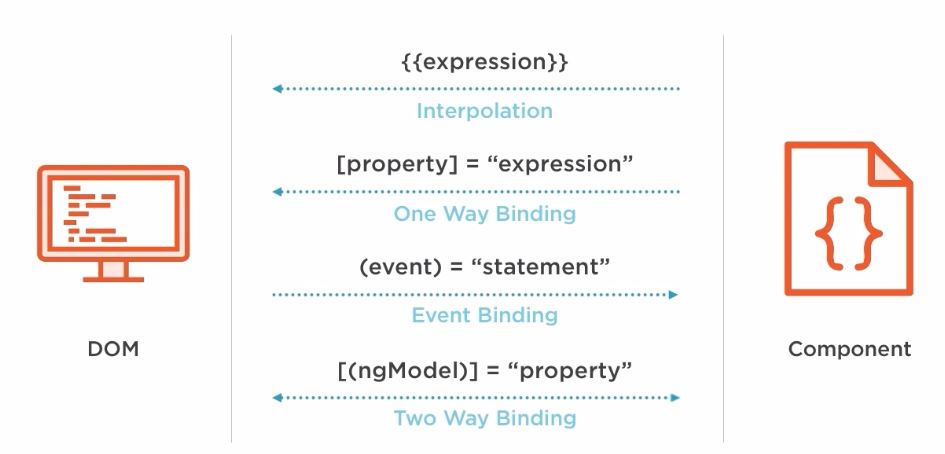
There are four forms of inter-component data binding syntax. Each form has a direction — to the DOM (source-to-view), from the DOM (view-to-source), or in both directions (view-to-source-to-view). It includes property, styles, and event bindings.
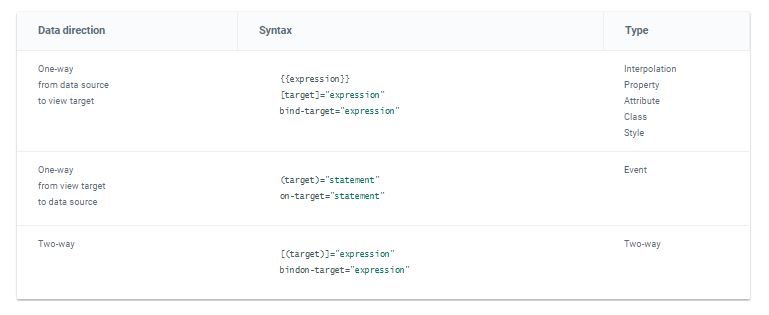
The following table summarizes all the types.
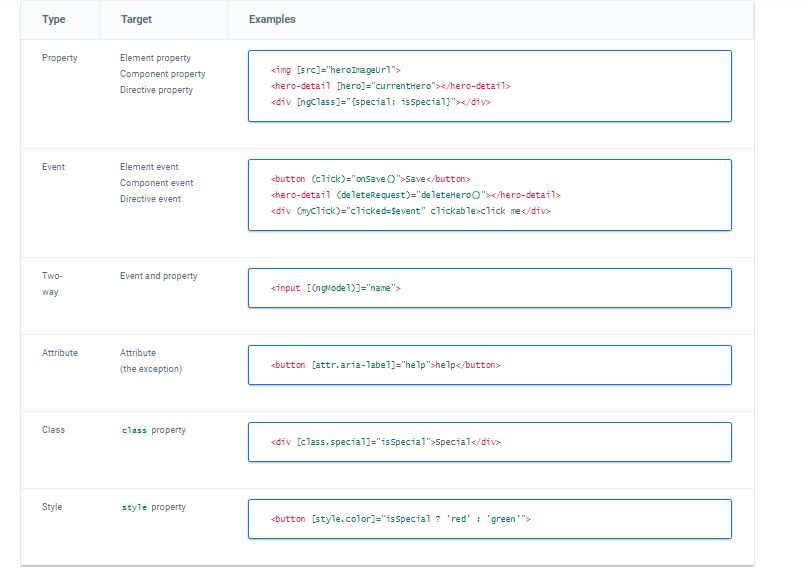
The following table summarizes all the types with examples.
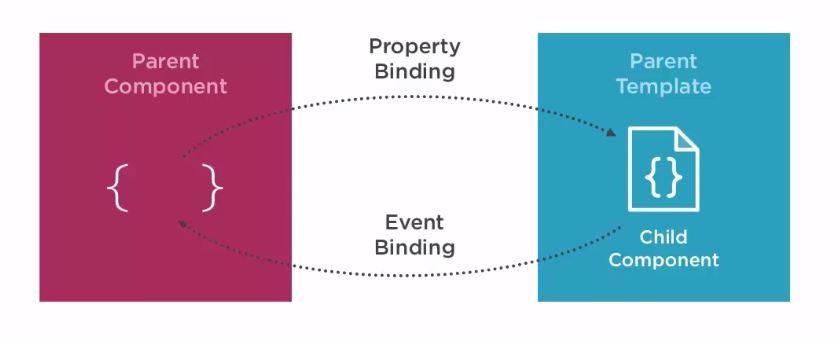
Parent-Child
parent-child is a communication between parent and child components in nested components (parent template refers to child component). We can use property binding to transfer data to the child component. In addition we can use event binding to activate some event in the parent component, depending on the child activity.
Across-Components
across-components is a communication between different components by using services. Service is a class with a well-defined purpose. It is independent from any particular component. It can be used to share data or logic across components. Services are defined outside components and they are injected to any component that needs it.
Services will be detailed in the Services lesson.