In this demo the ball follows the mouse movement.
Using mouse position, we calculate the ball position relative to its parent (the ball has absolute position inside its parent demo-blok). Then we change the ball position to the calculated value.
We use transition for the ball movement. Without transition, the ball will be sticked to the mouse location.
Note: since the ball is moving outside its parent container, we set the container 'overflow' property to 'visible' value.
Move the mouse, see how the ball moves.
Check 'Remove Transition' checkbox and see how the ball moves now without transition.
Check 'Change Overflow' checkbox and see how it moves now. When this checkbox is checked, the ball's parent demo-block 'overflow' property is set to 'hidden'. Thus, the ball will be seen only in the demo-block area.
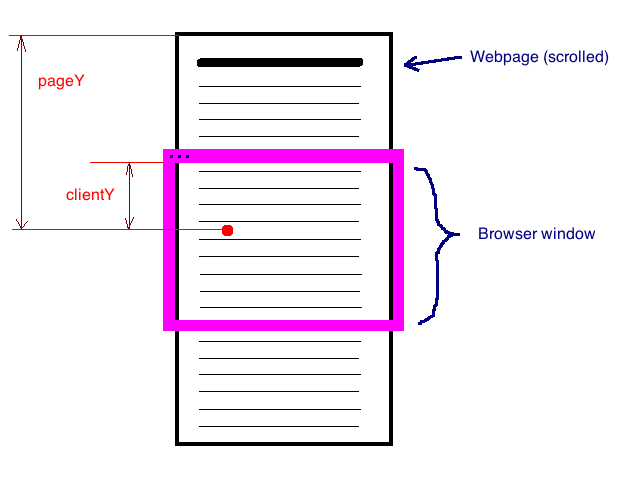
MouseEvent.pageX, MouseEvent.pageY, MouseEvent.screenX, MouseEvent.screenY, MouseEvent.clientX and MouseEvent.clientY return a number which indicates the number of "pixels" of the event point from the reference point. The event point is where the user clicked, the reference point is a point in the upper left. These properties return the horizontal and vertical distance from that reference point.

offset() - Get the current coordinates of the first element, or set the coordinates of every element, in the set of matched elements, relative to the document. offset() returns an object containing the properties top and left (vertical and horizontal locations).
To get the element location relative to the browser viewport use the folowing:
el = $('#my-element');
offset = el.offset()
elViewportOffsetTop = offset.top - $(document).scrollTop()
elViewportOffsetLeft = offset.left - $(document).scrollLeft()