There is a long list of text formatting tags.
These tags were presentation tags in previous HTML versions (the tags content have their own presentation on display like bold, italic, monospace ..., which we can change easily by CSS). In past HTML versions, for example <i> was for italic, <b> was for bold.
The main purpose of HTML is to add meaning to the webpages. The presentation will be done by CSS. With HTML5, a semantic meaning have been added to text formatting elements. Thus, if we use these tags, they must have a meaning in our document. For example, <em> browsers display as italic in the same way as <i> tag. However <em> has a different meaning, which can be other than italic in presentation.
Try to avoid these tags whenever possible, in order to make clean code.
A full list can be found in HTML Element Reference.
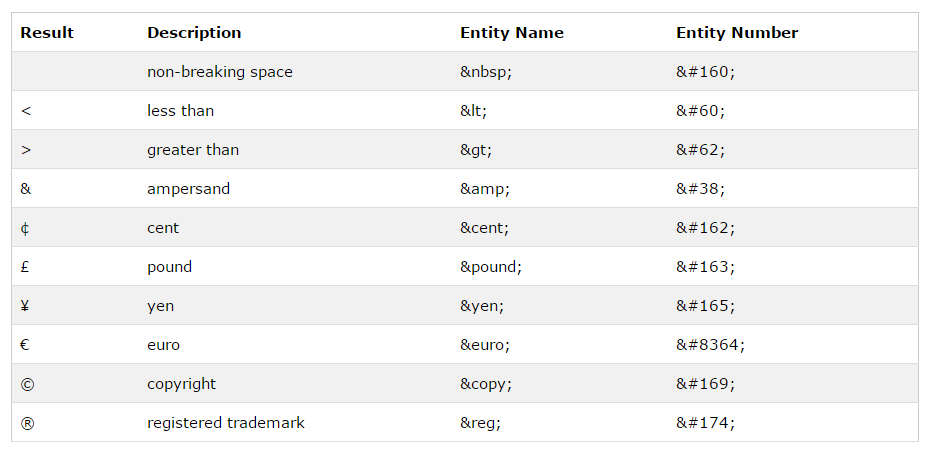
HTML is being used to write many different types of documents in many different languages. Therefore HTML documents may contain many different symbols that are not part of the standard alphabet.
To enable authors of HTML documents to include more symbols than are found in the ASCII table for example, or on the keyboard, HTML contains character entities. An HTML character entity corresponds to a symbol or character.
In addition, if we use for example the less than ( <) or greater than (>) signs in the text, the browser might mix them with tags. In this case we also use character entities to describe the symbol in the HTML code.
A common character entity used in HTML is the non-breaking space: & nbsp; A non-breaking space is a space that will not break into a new line. Two words separated by a non-breaking space will stick together at the end of a line. Another common use of the non-breaking space is to prevent browsers to truncate spaces in HTML pages. Normally the browser ignores multiple consecutive spaces and displays only one space. However, non-breakable spaces are always displayed.
We can write the symbol as entity name or as entity number.
Look here for official symbol list.
